Types of Printed circuit board is all around us. They are in almost all electrical devices; in fact, you are probably using one right now!
There are many different types of PCB, and they all have different applications. They are inside everything from life-saving medical devices to on board the space station.
In this guide, we explain all you need to know about types of circuit boards, how they are made and what PCBs are used for.
Table of Contents
Types of PCB Board
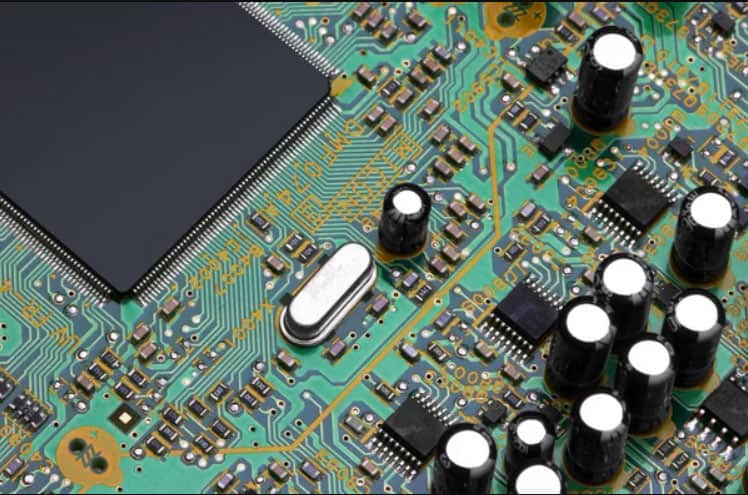

Caption: Closeup or electric circuit board
There are various types of printed circuit boards or PCBs.
Therefore, depending on the manufacturing process, application requirements, or specific design, a particular type of PCB board will be better suited to certain tasks.
These multi-functional boards are used in a wide variety of day-to-day and innovative industries.
As a result, they can be found everywhere, from inside your car to the interior of a spacecraft.
They come in a range of sizes, mechanical strength, and stability. But some are better able to handle stress than others.
The most common types of PCB are:
Single-Sided PCBs
Double-Sided PCBs
Rigid PCBs
Multilayer PCBs
Rigid-Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs
Single-Sided PCBs
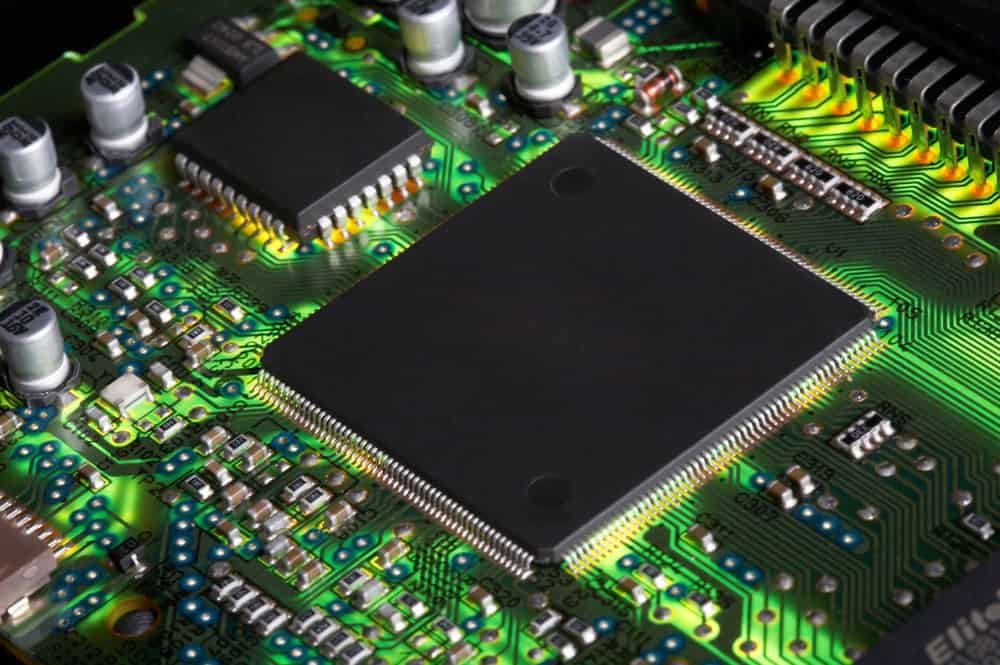

Caption: Closeup of PCB
Single-sided PCBs are the most widely used type of printed circuit boards. They have a singular layer of conductive copper on top of the substrate.
All of the electrical parts are fixed on a single side of the board and soldered in place to keep them secure.
The circuit is then etched onto the other side, where it’s clearly visible.
As this type of board only has one conductive layer, the electrical conduction paths are not able to overlap.
Therefore, they are quite wide and take up a lot of room. Consequently, single-sided PCBs are best suited for use in designs that have a low-density specification.
They are located inside many common electrical products, such as radios and calculators, for example.
As they are easy to manufacture and have a simple, low-cost design, single-sided PCBs are easy to repair or replace if something goes wrong.
Double-Sided PCBs
In double-sided PCBs, there are two thin layers of conductive material, usually copper. One layer is placed on each side of the board.
You can connect the metal components on either side via holes cut into the PCB.
Furthermore, as this type of PCB is double-sided, they are much smaller and take up less space than single-sided PCBs. They are then mounted in a through-hole fashion or surface mounted.
Through-hole mounting requires lead components to thread through the PCB holes and then soldered to the opposite side.
All components are accurately mounted onto the surface of the board to ensure the circuit will run efficiently.
Consequently, you can find this type of PCB located in amplifiers, cell phone systems, and other advanced electronic products.
Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs are very strong, but they are not flexible. The base of the board is manufactured with a type of rigid substrate.
It is then layered with copper, a solder mask, and a silk screen. Finally, all the layers are pressed together under heat to combine them into one durable board.
Rigid PCBs are very resilient and long-lasting. However, once manufactured, they cannot be changed or modified in any way.
Therefore, they are often used in equipment that requires reliable components. Some examples are heart monitors, MRI scanners, GPS navigation products, X-rays, and control tower instruments.
Multi-Layer PCBs
As the name suggests, multi-layer PCBs have a minimum of three conductive layers. Each of the double-sided layers is stacked on top of one another, just like a sandwich.
The layers are separated from each other by an equal number of insulation sheets. They are then laminated and bonded together.
This ensures that there are no air gaps. Accordingly, the final result is a stable and reliable product.
Multi-layer PCBs are commonly used. You can find them in laptops, cell phones, GPS trackers, computers, medical equipment, and many other complex electrical products.
Moreover, their compact size, robust construction, and flexible application make them ideal for high-speed circuits.
Rigid-Flex PCBs
Last but not least is the rigid-flex PCB. As you might expect, this type of PCB combines the best elements of both rigid printed circuit boards and flex circuit boards.
Rigid-flex PCBs can be bent and folded over and over again. The flexible piece of the board is generally used as an interconnector between the rigid sections of the board.
This allows for narrow conduction lines and creates a more streamlined, compact board.
This type of PCB is much lighter than a combination of rigid board and additional connectors. But their manufacture is more complex.
Rigid-flex PCBs are crafted in three dimensions. Therefore, the board can twist and fold as required to create the ideal shape for its application.
As rigid-flex PCBs are light, compact, and flexible, they are an excellent choice for medical products and use in the aerospace industry.
Flex PCBs
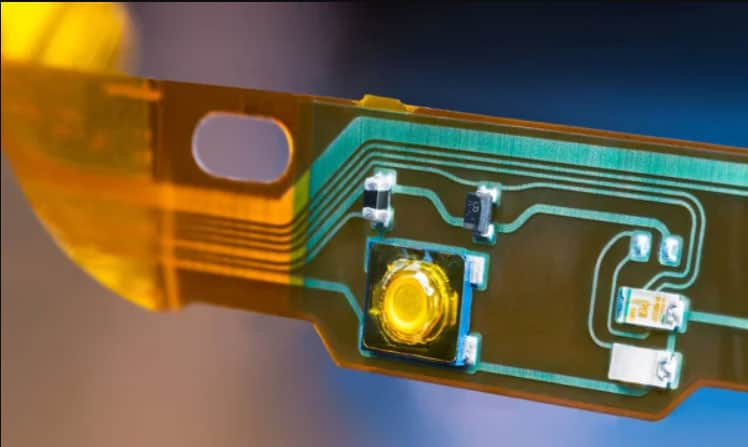
Caption: Flexible strip printed circuit
Flexible printed circuit boards are made up of a number of printed circuits and electrical components on a type of flexible substrate.
Usually, this is PEEK (polyether ether ketone) polyamide or transparent conductive polyester film.
Although they are made with the same electrical components as rigid PCBs, the substrate allows flex PCBs to bend and contort as required.
They are available as double-sided, single-sided, and multi-layer PCB types. Therefore, they can be used in all kinds of applications.
Due to their flexibility, this type of flexible PCB board saves space.
This makes them very useful for complex electrical products such as cameras, solar cells, vehicle manufacture, and much more.
How Are PCB Boards Made?

Caption: Engineer closeup with a microchip
Modern PCB boards are made from a variety of core components, the first of which is the actual board substrate. This is usually made by sandwiching at least two layers of material together.
Furthermore, conductive metal sheets are added. A layer of rigid non-conductive, insulating material separates these.
Let’s take a look at each section of a PCB board in more depth.
Types of Printed Circuit Board: Conductive and Masking Layers
Fine sheets of copper are most commonly used for conductive layers in PCB boards.
Depending on the type of PCB board, they are laminated to either one or both sides of the base substrate using high pressure, heat, and a specialized adhesive.
Once the board base layers have been created, the connector pathways that transport the electrical current are made.
These are called “traces”. The traces are etched into the surface of the copper layer.
As a result, they harness the high electrical conduction qualities of the material and create a complete circuit.
The copper layers must be very well insulated. Otherwise, rogue contacts interfere with the circuit and short it out.
The insulation should be provided by either further layers of a substrate or a solder mask that shields the external face of the board.
What are PCB Boards Used for?
This question is quite difficult to answer succinctly, as PCB boards are great for all manner of applications.
You could say that almost every electrical item on the planet has a PCB board inside it!
But in simplistic terms, PCB boards connect all the relevant components that a device needs to operate successfully.
This allows the device to function as intended and carry out complex processes smoothly.
Types of Printed Circuit Board: Electronic Devices

Caption: Woman using her mobile phone
The most common use of a PCB board is to allow an electronic product to perform a simple action.
They provide the required pathways and channels for signals and power to follow.
Consequently, if a device did not have a PCB board, the chances are that it wouldn’t even power up!
Types of Printed Circuit Boards: Computers

Caption: Fingers typing on keyboard closeup
Aside from these very basic tasks, with the addition of more components and higher-spec designs, PCB boards are able to perform more complex functions.
A good example of this is a computer motherboard. This type of PCB board is responsible for all the simple and detailed processes that a computer undertakes.
Furthermore, PCB boards are also crucial for the functioning of medical and industrial equipment, too.
FAQs
Types of Printed Circuit Board: What Does PCB Stand For?
PCB stands for “printed circuit board”.
Types of Printed Circuit Board: Can I recycle PCB Boards?

Caption: Green recycle symbol on gray background
Bare PCBs contain low amounts of copper, a conductive material that is recyclable.
Although some PCB boards contain other valuable metals such as silver, gold, and tin, the amounts are far too small to be worth anything.
However, the laminate layer PCB boards aren’t recyclable and must be scrapped.
What is the Difference between PCB and Semiconductor?
The most obvious difference between PCBs and semiconductors is size. Semiconductors consist of a small, flat piece of material with a tiny chip on top.
The chip contains a compact set of mini electrical circuits. They are often placed on the surface of a PCB and are used to connect electrical components across the board.
What’s the Difference Between PCB Board and Circuit Board?
PCB boards are blank circuit boards without any electrical components fixed to them.
Circuit boards are PCB boards with all the electrical parts installed that are required for them to function and perform the intended task inside a device.
Summary
It’s clear to see that PCB boards are critical to the technological lives we lead today.
These clever, compact, and crucial boards are found all around us in our laptops, computers, smartphones, and even vehicles.
We hope this article helped you to get a better understanding of different types of PCBs, how they are made, and their real-world applications.
Next time you use an electrical device, take a moment to appreciate the hard-working PCB board within it!