Types of diodes are the most common semiconductors found in electrical circuits. They are essentially dual terminal check valves ensuring power can flow only in one direction.
Diodes are usually made with silicon, but they are sometimes made with germanium, too. They have a huge range of applications and come in several different types with various important characteristics.
This guide looks at diodes, how they work, and what they are used for.
Table of Contents
- What is a Diode?
- Diode Symbol
- Diode Construction
- Types of Diodes
- Characteristics of Diode
- Diode Applications
- FAQs:
- Summary
What is a Diode?
Diodes are most commonly used to ensure an electrical current passes in one direction. At the same time, they prevent it from flowing in the opposite direction.
Simply put, a diode is an electronic version of a check valve. Its ability to create a unidirectional current is called “rectification”.
This quality is used to change alternating current (known as AC) to direct current (or DC).
When used in this manner, diodes are employed for tasks such as isolating modulation in radio devices.
Diodes also have more complex applications. They have nonlinear voltage qualities.
Therefore, their forward-direction voltage decrease only fluctuates minimally with current. Any drop is more a result of temperature.
Therefore, they are perfect for use in temperature monitors too.
Diodes have high resistance to a current that flows in the reverse direction.
However, this resistance can fall rapidly when the reverse voltage achieves a particular value called “breakdown voltage”.
In the case of semiconductor diodes, the current in the forward direction must reach a certain threshold before electricity is conducted.
Diode Symbol
Diode Construction
Diodes are formed by connecting two P-Type and N-Type semiconductors that are equally doped.
After they are joined together, the P-Type features extra holes and takes on a positive charge. Because of this, the N-Type then has an excess of electrons.
At their connection point, the P-Type holes attract the electrons from the N-Type. The electrons then move across into the holes within the P-Type.
Subsequently, this creates a flow of current in one direction.
Types of Diodes
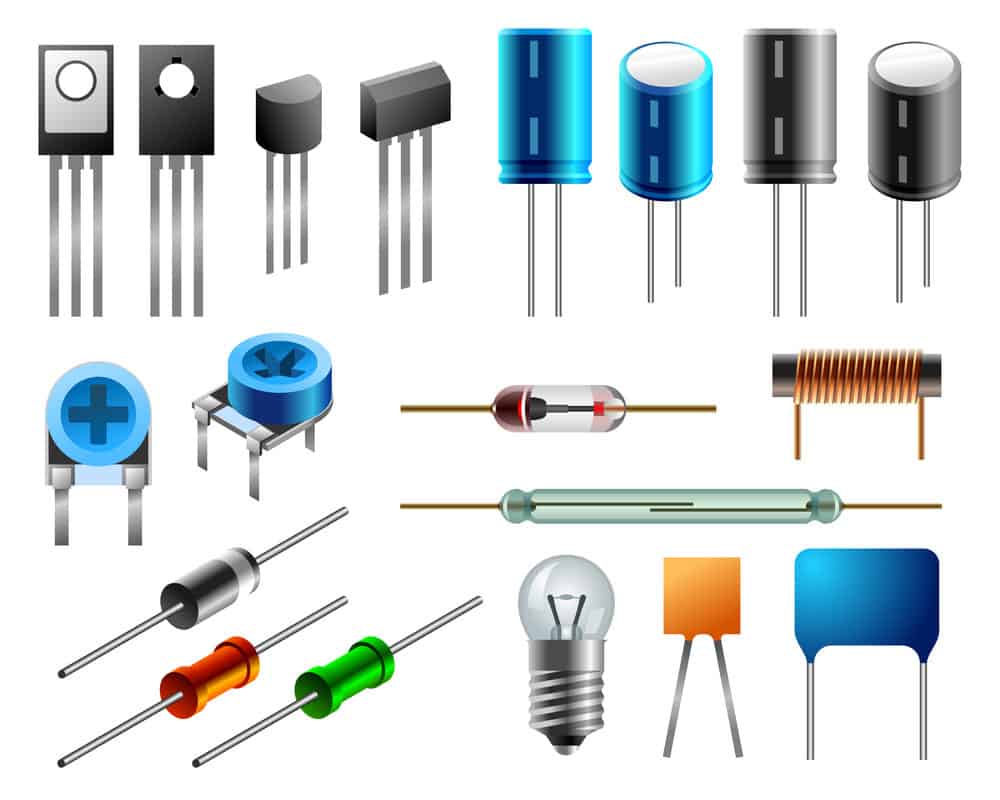
Caption: Types of diode and radio elements
There are several types of diode, let’s take a look at some of the most common types in more detail:
Light Emitting Diode
Caption: light emitting diode
Light-emitting diodes are formed from a semiconductor with a direct band-gap, usually gallium arsenide.
This junction is then crossed by charge carriers that emit photons as they connect to the other side. As a result, light is produced.
The type of light, whether it’s infrared or ultraviolet, is dependent on the type of material used.
Original LEDs had a red or yellow color. However, new diodes with a higher frequency have been developed.
All types of LED emit narrow spectrum light, and with different coatings and combinations, they can make a range of LED colors.
Semiconductor Diode
Semiconductor diodes are by far the most common type of diode. They are made from crystalline semiconductor material.
This material has a P-N junction attached to two separate electric terminals. In addition, the current-to-voltage characteristic is exponential.
This type of diode was the original semiconductor to be used in electronic products.
Transient-voltage-suppression Diode
This type of diode is specifically designed to shield other semiconductors against high-voltages.
Transient voltage suppression diodes have much bigger cross-sectional P-N junctions than average diodes.
Therefore, this enables them to conduct powerful currents without suffering damage.
Tunnel Diode
Tunnel diodes are able to show negative resistance as a result of quantum tunneling. This enables them to amplify signals.
They work incredibly fast, thanks to their very high carrier concentration. They can be used in high temperature, radiation, or magnetic field settings.
Therefore, they are frequently used in space technology.
Varicap
Varicap diodes are great voltage-controlled capacitors. Thus, they are critical in FLL (frequency-locked loop) and PLL (phase-locked loop) circuits, enabling tuning circuits to rapidly lock to a frequency. They also facilitated the early tuning of radio equipment.
Zener Diode
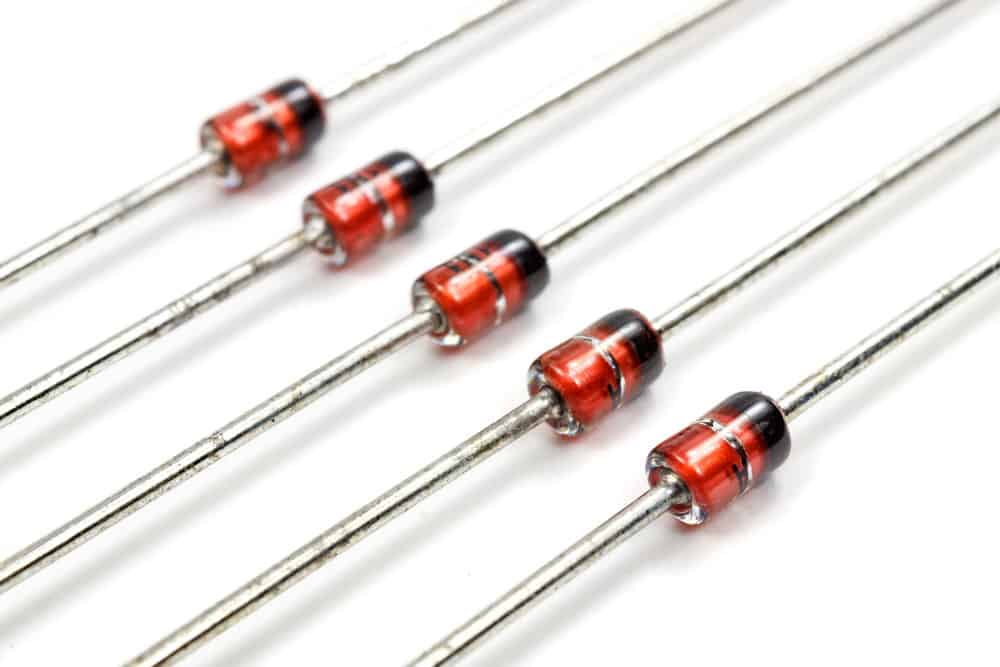

Caption: Zener diode
Zener diodes are semiconductor device made of silicon that allows a current flow in either direction.
This type of diode has a specialized P-N junction that is heavily doped. This allows it to carry current in reverse when a certain voltage level is achieved.
The voltage drop across this type of diode stays consistent. Therefore, it is often used for voltage regulation.
Characteristics of Diode
Diodes must block currents that flow in a reverse direction or behave as a short circuit if the current flow is in a forward direction.
However, the real-life behavior of diodes is not always as simple as this.
Diodes will consume some power as they direct and conduct a forward-moving current and don’t prevent all reverse-traveling currents.
Let’s look at some interesting characteristics of diodes and how they work in reality.
Forward Bias Characteristic of Diode
Forward bias describes when the P terminal has a higher positive charge than the N terminal.
In this case, the positive terminal of its battery acts as a repellent to holes or majority carriers in the P region.
It also repels electrons from the negative terminal in the N region – shunting them in the direction of the junction.
This leads to an increase in the number of charge carriers in the junction region. Electrons’ recombination occurs, and the depletion width in this region reduces.
Consequently, there is an exponential increase in the current.
Reverse Bias Characteristic of Diode
Reverse bias is when a P terminal connects to the negative terminal of a battery, and an N terminal connects to the positive terminal of a battery.
As a result, the N terminal has a greater positive charge than the P terminal.
The result is that the negative battery terminal attracts the holes, majority carriers from the P region, and the positive battery terminal gains electrons from the N terminal and attracts them away from the junction.
This activity leads to a reduction in charge concentration and a width depletion around the junction.
Diode Applications
Diodes are simple electrical devices used in a vast range of applications. They are found in almost every type of electrical circuit. Therefore, their importance shouldn’t be underestimated!
In this section, we look at some of their most common uses.
Rectifiers
Rectifiers are circuits that convert AC (alternating current) into DC (direct current). This currency conversion is required for all manner of common electronics.
Alternating current signals flow from your household power outlets. However, it is the direct current that powers most electrical devices.
Do you see the problem here?
AC behaves exactly as its name suggests – it alternates! It switches backward and forwards between positive and negative.
On the other hand, DC moves in just one direction.
It must be prevented from flowing backward to convert AC and make it move in one direction. This is what diodes are for!
Reverse Current Protection
Sometimes you must prevent a current from going backward to protect a circuit.
If a diode is used on the positive side of a circuit, it will stop the current from moving in reverse. This ensures that the power can only flow in a positive direction and provides positive voltage within the circuit.
Flyback Diodes and Voltage Spike Suppression
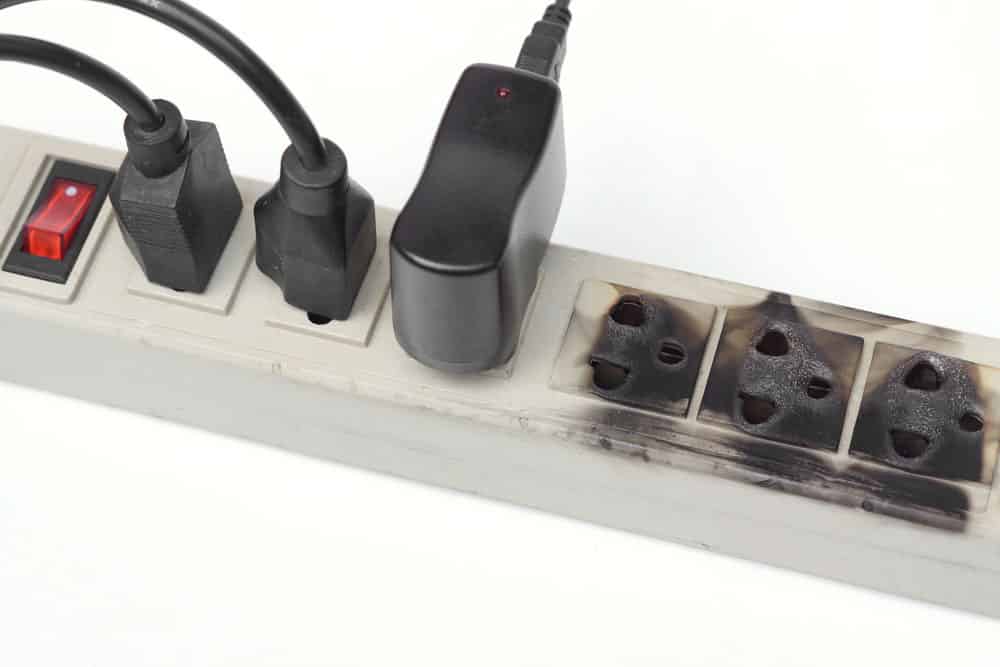

Caption: surge protector burnt
Diodes are commonly used to shield against damage caused by sudden voltage surges. TVS (transient voltage suppression) diodes, as explained above, are a special type of diode.
They are rated to withstand incredibly high voltages, so they can “push” it back if a surge occurs.
In extreme cases, a TVS diode will absorb the excess voltage, thus protecting equipment further down the line.
FAQs:
Are Diodes AC or DC?
Diodes only work in DC (direct current) as they are unidirectional electrical devices. Therefore, they are designed to only allow current to move in one direction.
What are the 3 main uses of diodes?
The three main uses of diodes are rectifiers for reverse current protection and voltage spike suppression.
Can a diode be used as a rectifier?
Yes. Diodes are commonly used as rectifiers.
Which is a common type of diode?
The most commonly used type of diode is a rectifier diode. This diode has a large P-N junction area and converts AC to DC for most household electronics.
Summary
Caption: AC to DC
Diodes are relatively simple devices but incredibly useful in our daily lives.
The clever components can control the flow of electrical currents, ensuring that they travel only in one direction.
They are commonly used to convert AC to DC. Therefore, you can use all your favorite household appliances without problems.
Diodes are also crucial to protect against power surges that can cause devastating damage to equipment and infrastructure.