Flexible printed circuit boards, also known as flex PCBs, are one of many variants of PCBs.
They get their name because they can bend, but there are other significant differences between standard and flex PCBs.It includes design, functionality, and fabrication.
Flexible printed circuit boards have become far more complex over the years. Many industries across the board have incorporated them into their manufacturing processes.
In this article, you’ll learn about the most common types of flexible printed circuit boards used today.
You’ll also know what makes them unique and why they’re essential to electronic devices across various sectors.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Flexible Printed Circuit Board?
- Benefits of Flexible Circuit Boards
- Disadvantages of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
- Applications of Flexible Circuit Boards
- Types of Flexible Circuit Boards
- Materials Used in Flexible Circuit Boards
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What Is a Flexible Printed Circuit Board?
A flexible PCB board has a metallic layer of traces bonded to a dielectric layer. These traces are usually made of copper, while the dielectric layer is made of polyimide.
Manufacturers often use an adhesive to bond the metal and substrate. However, other types of bonding, like vapor deposition, can also serve the same purpose.

Copper wire
Because copper oxidizes quickly, its exposed surfaces often get covered with a protective layer, solder and gold being the two most common materials.
It is due to their combination of environmental durability and conductivity. In non-contact areas, manufacturers use a dielectric material to protect the circuitry from electrical shorting and oxidation.
Benefits of Flexible Circuit Boards
Ultra-thin flexible PCBs have many applications, including;
Reducing Assembly Errors
Flex circuits eliminate most human errors thanks to their highly accurate designs and automated production process.
Faster Assembly Time and Lower Costs
Flex circuits don’t need as much manual labor during assembly. Furthermore, it reduces production errors, so the product gets rolled out faster.
Flex circuits can also integrate fit, form, and function. Routing, wrapping, and soldering wires in circuit boards are expensive. Because there are no wiring errors, manufacturing costs reduce significantly.
Repair of electronic components
Freedom in Design and Layout
Flexible circuit boards offer manufacturers a lot of freedom in design. Unlike rigid boards, a flexible PCB board isn’t restricted to two dimensions.
Moreover, they’re as flexible as wires, so the design options for flexible circuit boards are limitless. Technicians can design flexible circuits to meet highly specific and complex configurations.
Again, these configurations can operate even in the most hostile environments.
Disadvantages of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
They’re Expensive
Flexible printed circuit boards have a high initial cost. It is because of their specialized nature and the intensive manufacturing processes required to produce a unit.
Difficult to Repair and Replace
Due to its complex structure and applications, repairing a flexible printed circuit board is complex. In addition, changing the flex PCB is also hard. It is because it has a protective film you must remove before switching out any parts.
Size Restrictions
Because of their structure, design, and applications, manufacturers can only produce flexible PCBs that are large and narrow.
Susceptible to Damage
Flexible PCBs are more sturdy than standard PCBs. It’s easy to break or damage them during installation.
That’s why it’s important to seek out professionals when you want to repair, change, or install a flex PCB.
Applications of Flexible Circuit Boards
Because of their physical attributes, flexible circuit boards feature widely in products that aren’t likely to remain stationary.
Combined with their durability and size, this feature makes them useful for many industries. Some of the applications include;
Automotive Industry
As manufacturers venture into the EV market, the automotive industry has increasingly turned toward electronic components.
Electric cars need circuits capable of withstanding the vibrations and stresses of a vehicle’s interior.
Moreover, a flexible printed circuit board offers car companies a valuable option for their needs, one that is durable yet cost-effective.

Electric cars charging station
Medical and Healthcare Systems
There’s an increased demand for smaller and denser electronic designs in the medical industry. It is due to the popularity of handheld surgical technology and wearable electronics like implants.
Therefore, flexible PCBs can bridge the gap between size and durability requirements for medical technology.
Power Electronics
Flexible printed circuit boards can work with highly flexible, ultra-thin layers of copper that can handle much stronger electrical currents.
That’s an essential feature in devices that need more power to operate at maximum capacity. Think of devices used in the power electronics industry.
Consumer Electronics
Small electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, cameras, GoPros, and similar gadgets use flexible PCBs. These products often get transported or handled in rough conditions.
Therefore, it makes the flexible PCB’s resistance to vibration and shocks an attractive feature.

GoPros action camera
Industrial Applications
Industrial electronics get exposed to massive amounts of stress and vibration. Therefore, flexible PCBs with shock absorption and anti-vibration capabilities are helpful for heavy industrial equipment.
LED Lighting
LED lighting is everywhere, from residential to commercial areas. It is because LED technology is power-efficient; however, the only concern is heat.
On the other hand, flexible printed circuit boards solve this problem with their effective heat transfer qualities.
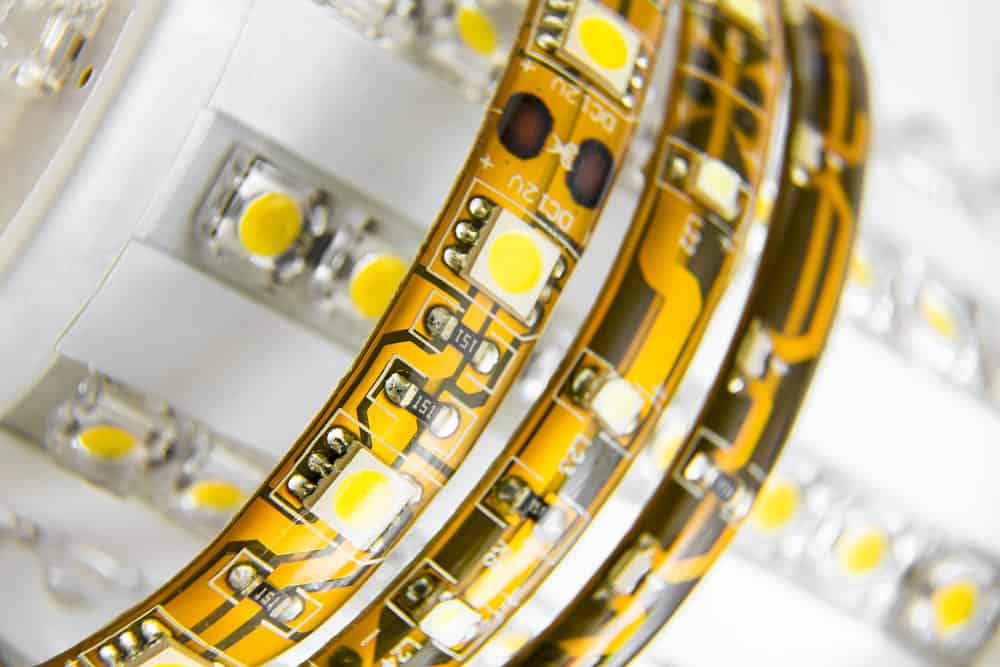

Different LED strips on LED bulbs
Types of Flexible Circuit Boards
Single-Sided Flex Circuit Board
These are the most basic and common types of flexible PCB boards. They have one layer of metal traces on one side of a dielectric layer. This dielectric is usually made of polyimide or polymer.
Moreover, a polyimide overlay adds extra insulation to the board and protects copper tracing from environmental degradation.
Double-Sided Flex Circuit Board
Double-sided flex circuit boards have two conductive layers—one on both sides of the polyimide base layer within the circuit. You can also create trace patterns specific to your needs on both sides of the substrate film.
Multi-Layer Flex Circuit Board
Multi-Layer flex circuits have multiple copper layers separated by dielectric layers. These metal layers get connected by through-holes drilled into the board.
Therefore, they can support more complex interconnections and are suitable for layer design surface-mounting.
Rigid Flex Circuit Board
Rigid-flex PCBs have several circuit layers connected by a bonding film made of epoxy. It’s similar to a multi-layer flex circuit. However, rigid-flex circuits have a much higher component density.
Materials Used in Flexible Circuit Boards
Insulating Layer
The insulating layer or insulating film is the foundation for the flexible PCB. It also protects the board from moisture and dust and minimizes strain when flexing it.
Conductive Layer
Most PCBs use copper foil as their conductive layer. It’s usually electroplated or electrodeposited. Manufacturers prefer copper foil because it’s flexible enough to get shaped in many ways yet rigid enough to maintain its form.
Adhesive Layer
The adhesive layer serves three functions:
- Bonding the insulating layer to the copper foil
- Protecting the circuit board components from damage
- Covering the board’s surface
Not all boards have an adhesive layer, but it’s a common feature in flexible PCBs.
FAQs
What Is the Difference Between PCB and PWB?
A PCB has its circuitry intact and is a finished product. A PWB is a board without any components.
What Are the Different Types of PCB?
PCBs come in several variations. The most common ones are single and double-sided PCBs. There’s also the multi-layer, rigid, flex, and rigid-flex PCB.
Is Flex PCB More Efficient?
Yes. Flex PCBs cut costs on production and human error. They’re also more versatile in their applications, offering more value for money.
Why Are Flex PCBs So Expensive?
Flexible PCB manufacturing is lengthy and complex. Furthermore, it requires a unique environment and materials, which make the finished product more expensive.

PCB manufacturing
Conclusion
Originally designed to replace traditional wire harnesses, flexible printed circuits have come a long way.
Their design continues improving, and their applications in various industries expand yearly from connectivity and mobility to wearable tech and communications devices.
Their versatility is unmatched, taking on simple and complex applications with ease. And with their many additional features, they’re well worth the extra expense.
No other PCBs will give you the high-density application, flexible installation, and increased system reliability that flexible printed circuit boards offer.