What Are Printed Circuit Boards Used for? If you’re a fan of sci-fi flicks, at some point, you’ve probably seen a little green chip with bits of shiny metal and wires stuck onto its surface.
It’s called a printed circuit board or PCB, and it’s a crucial part of almost every electronic device you know, from your personal computer and smartphone to your TV and car key remote.
PCBs feature in the tech sector that experts project the global market will grow to $76 billion by 2024. Recent advances like 3D printing have led to a boom in the industry, making it possible for their production on a scale never seen before.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Printed Circuit Board?
- Why Use a Printed Circuit Board?
- Applications of Printed Circuit Boards
- What Are Some of the PCB Assembly Options?
- What Are the Most Common Uses of Printed Circuit Boards
- FAQs
- Conclusion:
What Is a Printed Circuit Board?
In simple terms, a PCB is a mounting surface or base for electronic and mechanical components. Most PCBs contain plastic or glass-fiber and resin composites and use copper traces. However, various other materials may also get used in their construction.
In appearance, they’re usually flat and rigid yet flexible enough to fit in convoluted spaces.
Moreover, this board has electronic component mountings, and the traces connect them to form a working assembly or circuit. Therefore, they allow automated assembly processes that weren’t possible or even practical with earlier model tag-type circuit assembly processes.
Circuit boards come in many forms. Single-sided PCBs contain one copper layer above the substrate, the most common circuit board type. Double-sided PCBs have a copper layer on the top and bottom of the substrate.
Finally, multilayer PCBs have more than two layers of copper arranged in a ‘sandwich’ pattern, alternating with substrate layers.
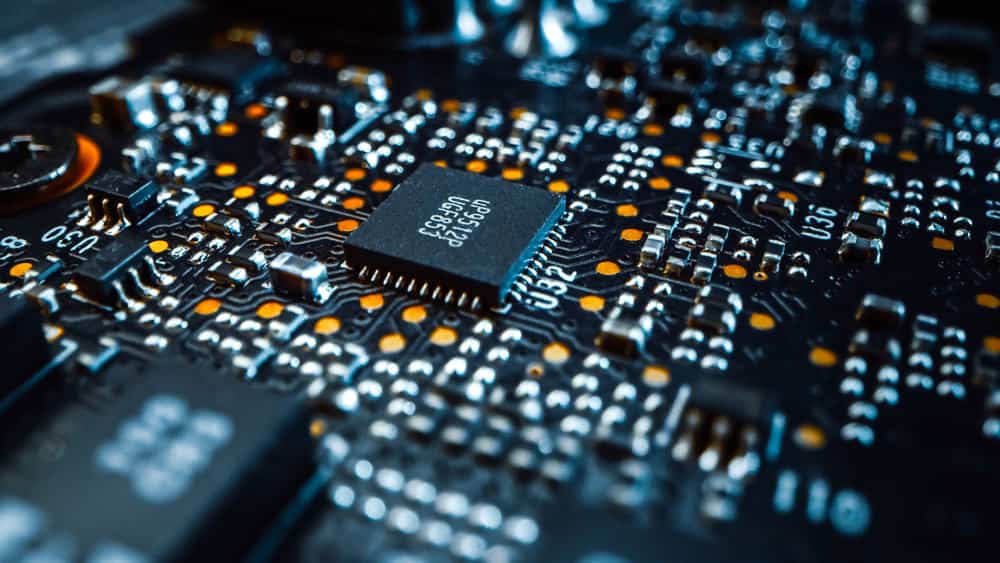
Macro- closeup shot of PCB
Why Use a Printed Circuit Board?
The primary function of a circuit board is to provide mechanical support and electrical connections to the electrical components mounted onto its surface. Therefore, they’re vital in computers, playing a role in the system’s performance, reliability, area, power, and security.
Applications of Printed Circuit Boards
Electronic Devices
Consumer electronics is the most common sector for printed circuit boards.
Whether it’s your television, microwave, video game console, or even a coffee maker, most electrical appliances and home entertainment systems have a circuit board inside them.
You’ll also find PCBs in communication devices like smartphones, smart watches, tablets, and radios.

Woman in a shirt using a microwave in the kitchen
Industrial Applications
Printed circuit boards are vital in businesses with manufacturing facilities and production lines. In these sectors, circuit boards enable automation that helps businesses reduce human error while saving on costs.
Some examples of industrial equipment that use PCBs include assembly machines, ramps, presses, and any equipment with electrical components.
Power equipment like power suppliers, inverters, power distributors, and other power control devices also use circuit boards in their foundations.
Furthermore, precision equipment that controls the temperature, pressure, and other variables in the manufacturing process relies on circuit boards to keep things running smoothly.

Industrial electricity inverters
Medical Equipment
Printed circuit boards contribute to the medical sector. They’re used in appliances, treatment, diagnostic, and monitoring devices. The applications of PCBs for the medical sector continue to grow as technology improves and opens up new possibilities.
Scanning equipment like ultrasonic scans, CT scanners, and X-Ray screens use circuit boards to maintain electrical components. Besides scanners, medical devices such as heart rate and blood and glucose monitors also use PCBs.
In addition, circuit boards work inside diagnostic tools like control systems, compressors, electronic microscopes, and other devices.
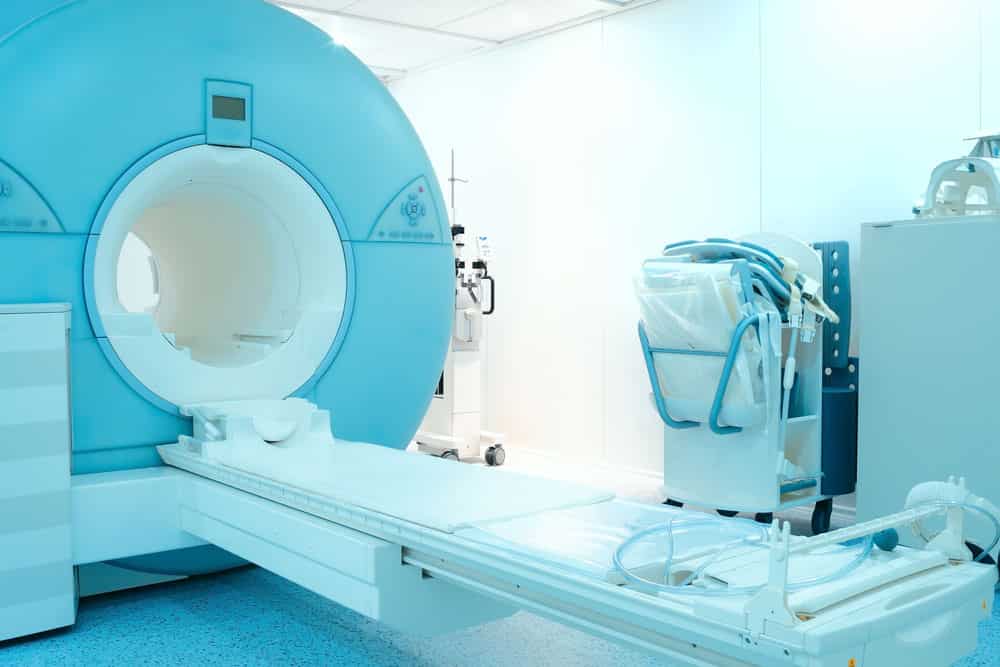
CT machine
Automotive Industry
Most modern cars now have a range of electrical parts and advanced electronics that offer extra features. It’s a sharp contrast to the old days when cars only had a few electronic circuits for essential functions.
Because of these technological advances, circuit boards have evolved with the automotive industry.
Vehicle navigation systems such as satellite navigation have become common in modern vehicles. All of these systems use PCBs.
Cars with advanced dashboards that connect to the vehicle’s radio or media player also use electronic parts built on circuit boards.
In addition, sensors that monitor fluid levels and engine health couldn’t do their job without PCBs.
What Are Some of the PCB Assembly Options?
When assembling PCBs and their components, you’ve got two options: through-hole and surface mount.
Through-Hole Mount
With THM or through-hole mounting, the assembler places component leads through holes drilled into the PCB. This outdated method isn’t commonly used today.
THM has a strong connection because the leads run through the board, but working with this type of mounting technology takes a lot of time and effort.
Surface Mounting
With surface mounting, the assembler connects the components directly to the PCB through soldering, where heat joins metal parts to form mechanical or electrical bonds.
Introduced in the 1960s, it grew popular in the 80s. It’s the most commonly used method today. Because they’re smaller, surface-mounted components can fit more pieces on a circuit board.
This is why many electrical devices have become smaller over the years.
What Are the Most Common Uses of Printed Circuit Boards
Aeronautical Engineering
PCBs feature in the aerospace industry, from planes and satellites to space shuttles and communication systems. Some circuit boards get built for use in outer space.
Therefore, they must have even more durability. Then there are lightweight PCBs made of aluminum.
This combination of lightness and durability can prove quite useful in some situations, such as in electronic components on rocket ships, which must have as little extra weight as possible.
Security and Surveillance Equipment
Circuit boards get used in cameras, electronic door locks, smoke detectors, motion sensors, and heat or pressure sensors.
LED Lighting
LEDs or light-emitting diodes get used in commercial and residential areas. PCBs work well for LEDs because they transfer heat away from the bulb, preventing them from burning out faster,
FAQs
What is PCB in Electronics?
A PCB is a device used to support and electrically connect electrical components mechanically.
What Are the Types of PCB?
There are six types of PCB. The most common is the single-sided PCB and double-sided PCB. More complex devices use multilayer PCBs.
Rigid PCBs can’t get bent or flexed, while flex PCBs can bend and stretch to accommodate coils and wires. Rigid-flex PCBs combine all the qualities above.
What Are Printed Circuit Boards Used for: What Material Makes PCB?
The three materials used to make PCB include glass, resin, and copper.
What Is the Purpose of a Printed Circuit Board?
Printed circuit boards are the foundation or base for electrical components that power a device, such as phones and computers.
Conclusion:
Today, PCBs in electronics remain the most common and popular way to create new products. They’re why your smartphone is slimmer, and you can fit 1 terabyte of memory in a small disk the size of your thumb.
Circuit boards continue to revolutionize various industries, cutting costs, streamlining complex processes, and sometimes even helping save the environment by developing eco-friendly, recyclable components.
Only time will tell what else they’ll improve in the future.